Table of Contents:
Are Worker Bees Male or Female?
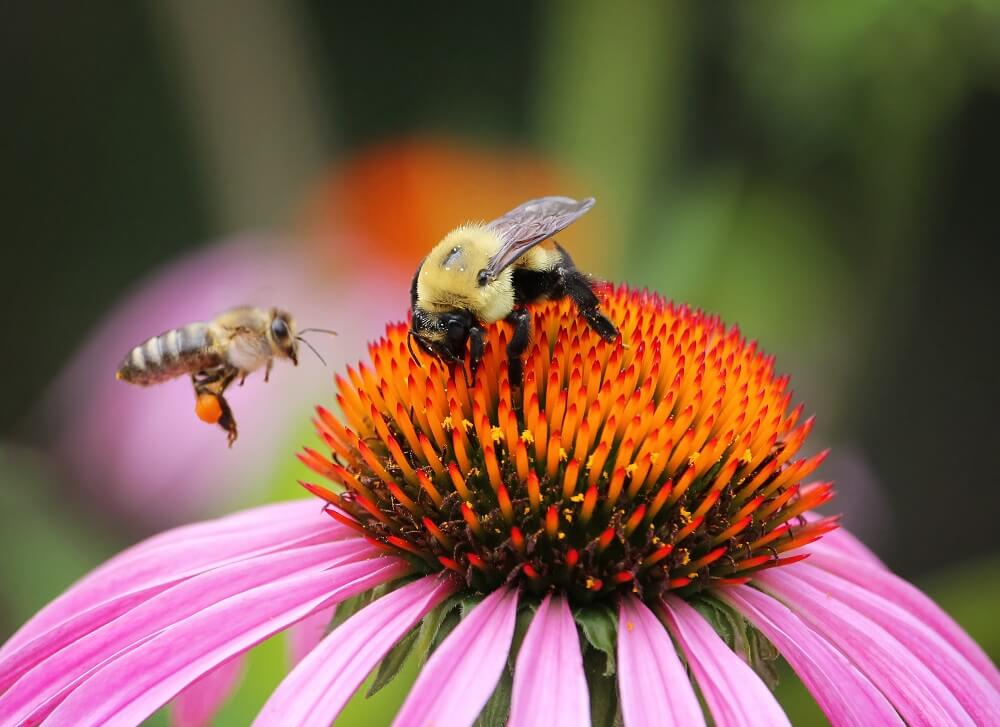
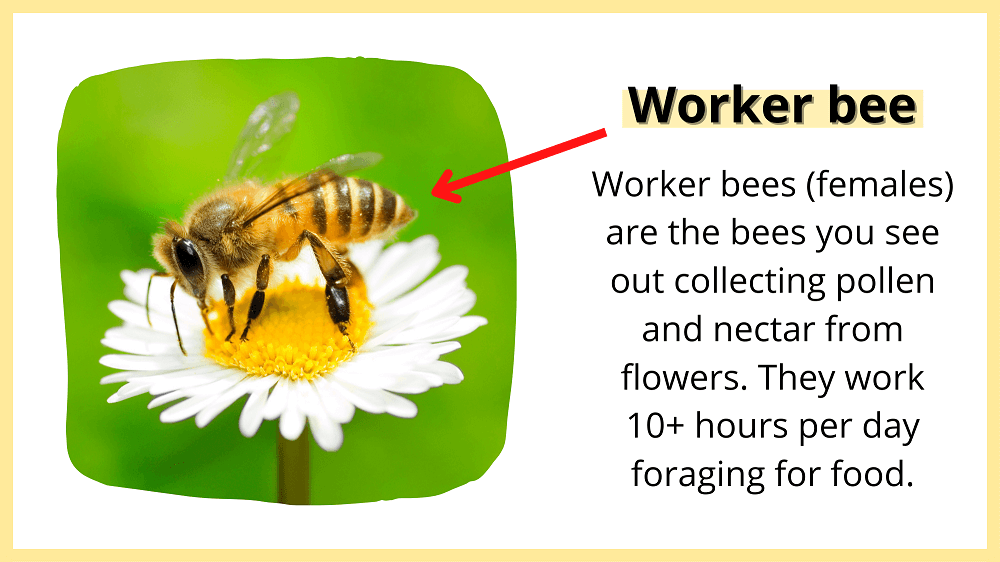
Worker bees are female bees responsible for most of the work in the hive. Their duties include cleaning and protecting the nest, as well as feeding the queen, drones, and baby bees.
Now you might be asking:
Wait, so are all worker bees female?
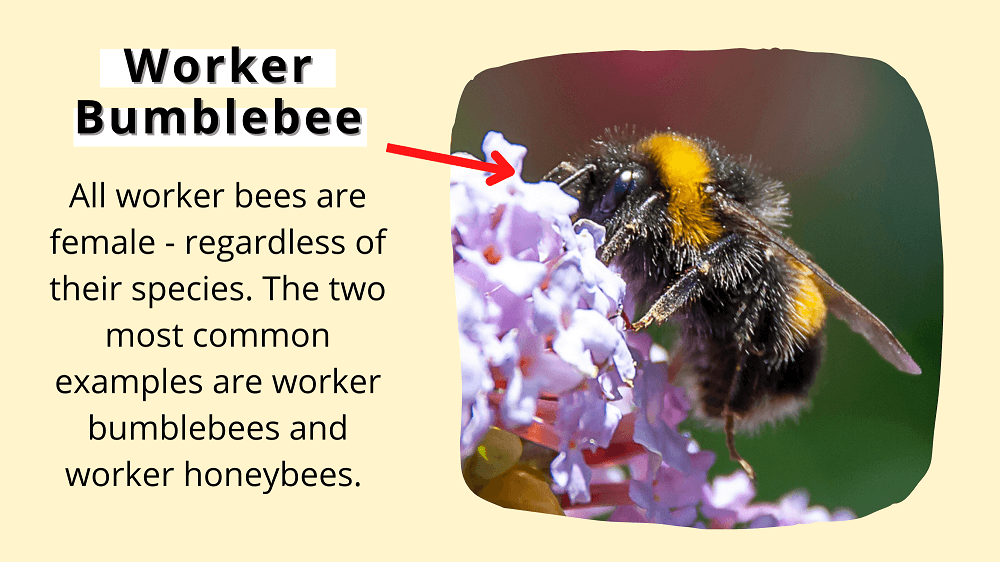
Yes, worker bees are exclusively female, and they make up the majority of the colony.
And let me reiterate:
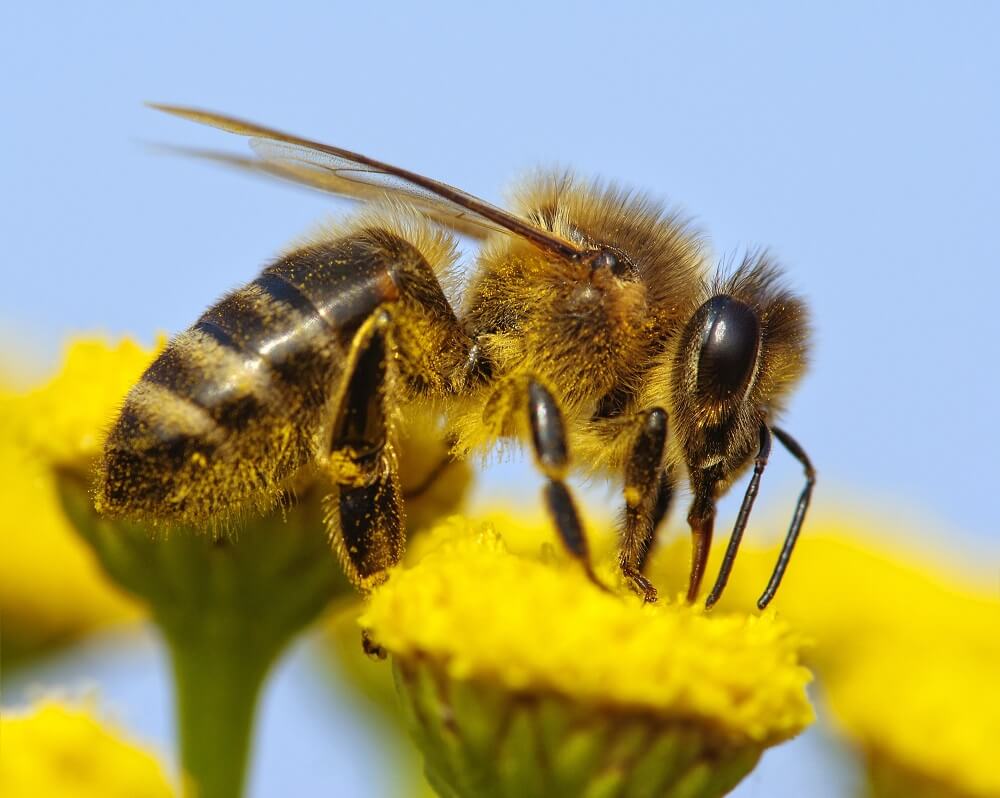
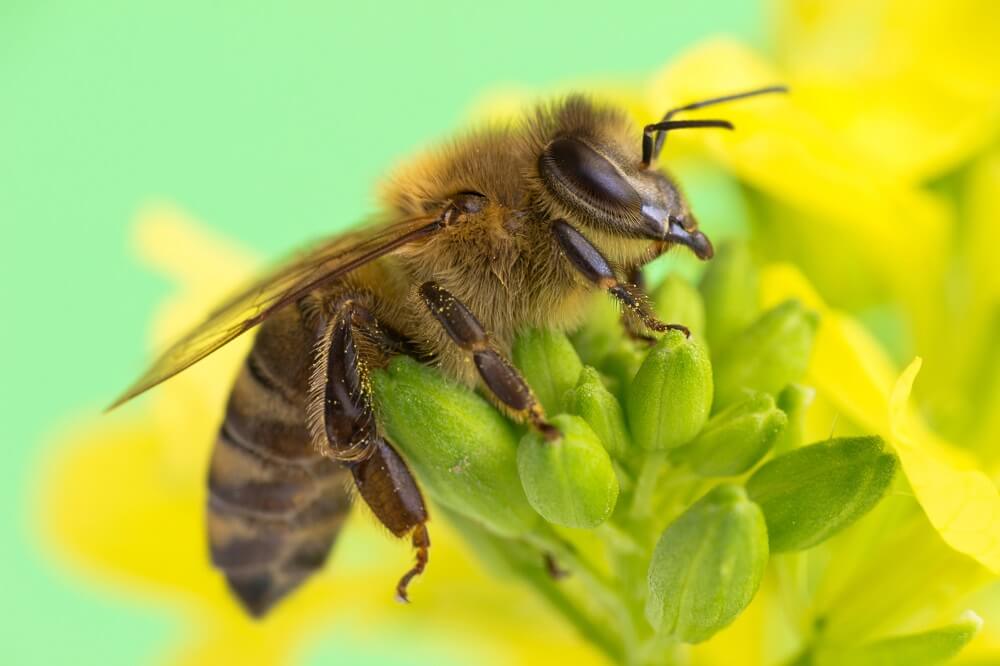
Worker bees do most of the heavy lifting. For example, the bees you see buzzing around flowers are most likely female worker bees. This is because one of their main job duties is to collect food for their hive. So they’re out and about busily collecting pollen and nectar.
Now here’s something that might surprise you:
Only female bees can sting. Male bees can’t sting because they don’t have stingers.
Why?
Because stingers are modified egg-laying devices, so male bees never developed them. This means if you’ve ever been stung by a bee, it was by a female.
So what do male bees do?
Well firstly, male bees are called drones. They don’t collect food for the hive, clean, or build and maintain the nest. And since drones don’t have stingers, their ability to protect the hive is limited.
That said, drone bees have one very important purpose:
To mate with a new queen.
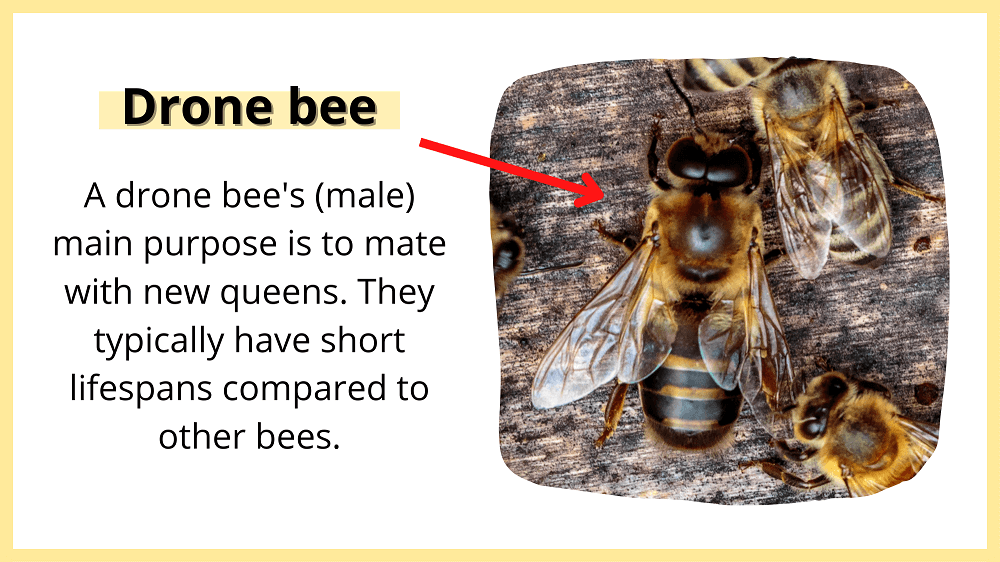
Because of this, drone bees tend to have very short lifespans compared to other bees. Their purpose in life is simple, so they don’t need to hang around very long to accomplish it.
Some species of drone bees – such as drone honeybees – die immediately after mating. Other drone bee species – like drone bumblebees – can mate multiple times without dying.
Either way, drone bees still typically have the shortest lifespan of any other bee in the colony.
Take bumblebees as an example.
Worker bumblebees live 28 days on average. Drone bumblebees only live for about 14 days. If you do the math, this means that worker bumblebees live twice as long as drone bumblebees.
And worker bumblebees have a lot to accomplish in their short 28-day lifespan.
Speaking of that…
What Do Worker Bees Do?
People are often surprised to learn that worker bees are female. And when they learn, their main question becomes:
So what do worker bees do?
Worker bees do almost everything for their colony.
But let’s start with the one very important thing worker bees can’t do:
Lay fertilized eggs.
In bee colonies, there are three roles:
- The queen bee
- Worker bees
- Drone bees
The queen bee’s main priority is to ensure another generation of bees by laying eggs. Drone bees help queens accomplish this by mating with them. As a result, this tasks worker bees with the rest of the work both inside and outside the hive.
Now I want to clear something up really quick:
Worker bees can lay eggs, but only unfertilized ones. This is because, unlike queen bees, worker bees never mate with drone bees, so they don’t become inseminated. As a result, they can’t lay fertilized eggs like queens do.
The colony’s future depends on fertilized eggs. So without a queen and drone bees, the colony will soon collapse.
So now back to the original question:
What do worker bees do?
Here’s a list of their main job duties:
- Worker bees collect food and water for the hive. Bees eat pollen and nectar from blooming flowers. Pollen is a bees’ main protein source, and nectar is their main carbohydrate source. Worker bees that forage for food and water are called “forager bees.” They have a tiring job because they work from sunup to sundown.
- Worker bees nurture and feed baby bees. These worker bees are called “nurse bees” because they tend to the queen and developing larvae. They feed, clean, and remove their body waste from the hive. They even encourage the queen to lay eggs.
- Worker bees protect the hive. These worker bees are called “guard bees.” They secure the hive entrance to deter intruders. For example, wasps will often try to enter a honeybee hive to kill the bees and steal their honey. A healthy honeybee colony will form a “bee ball” around the wasp, overheating the intruder until it dies. And believe it or not, these “bee balls” can get as hot as 115°F (46°C).
This isn’t an exhaustive list of what worker bees do because different species of worker bees do different things.
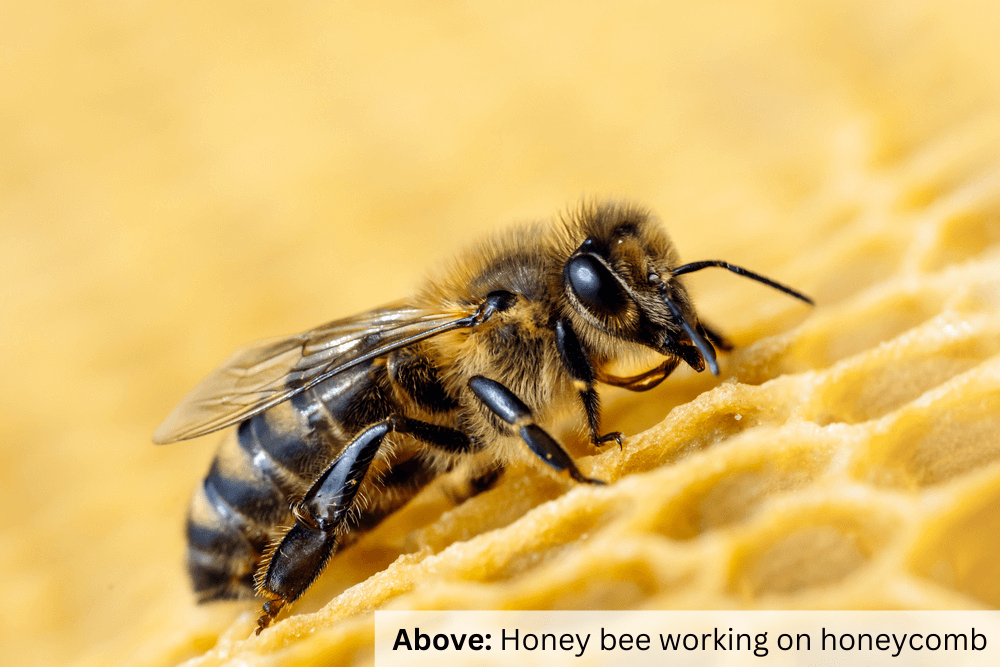
For example, worker honeybees are also tasked with building combs and making honey. This is a unique job that worker honeybees have since most other types of bees don’t make honey.
Now you might be thinking:
How Do Bees Assign Job Duties?
Does the queen bee come off her royal throne to assign job responsibilities?
Not exactly.
A worker bee’s job is determined by her age.
Older and more experienced worker bees are the ones who forage for food and guard the hive. Younger and less experienced worker bees clean the nest and tend to the baby bees.
As a result, a worker bee will eventually experience every job in the hive. However, this doesn’t mean she does all the jobs at once. Instead, she graduates to a new role as she gets older. And once she gets a new job position, she focuses on that position until her next “promotion.”
Eventually, the worker bee will age and pass away. New bees take her place, and the cycle continues.
So, where does it all begin?
Truthfully, it depends on the bee species. But let’s use honeybees for this example.
Newly hatched worker honeybees become nurse bees. Their job is to take care of the queen and larvae by feeding and grooming them. They also clean the hive, build comb, and make honey. This job role usually lasts about three weeks.
Next, nurse worker bees move onto the role of guard bees. Guard bees are responsible for watching the entrance and inspecting bees entering the hive. They sting intruders and release alarm pheromones to warn the colony of potential danger. This role typically lasts a few days.
And finally?
Worker bees eventually graduate to forager bee status. This means they start collecting pollen and nectar for the hive. Foraging for food is a strenuous job because they’re exposed to the natural elements and other predators. Flying around also takes a toll on their wings and bodies.
The forager bee role usually lasts about three weeks until the bee eventually passes away.
Related: Honeybees vs. Bumblebees: How Do They Compare?
4 Interesting Facts About Worker Bees

1. Honeybees are considered livestock by the USDA
Say what?
Yes, you read that right.
The USDA refers to beekeeping by its agricultural name – Apiculture. They point out that honeybees produce various products that can be sold, with the most common being honey and beeswax.
The USDA also mentions that beekeepers can earn money through selling bees to other beekeepers and renting out beehives to farmers for crop pollination.(1)
More importantly?
Bees add an estimated $15 billion worth of value to crops every year. This is because when bees pollinate crops, they increase the yield and quality.
Bees even help self-pollinating crops like tomatoes and cotton. Self-pollinating crops technically don’t rely on pollinators. That said, self-pollinating crops produce more and better qualities with the help of bees and other pollinators.(2)
Related: How Many Eyes Does a Bee Have?
2. Worker bees make all the decisions for the hive

Sometimes people think the queen bee rules the roost.
But this isn’t the case at all.
A beehive acts more like a democracy, with the worker bees coming to a consensus about various things, including:
- Where to forage for food
- When and how to expand the nest
- When to raise new queen bees to replace the old one
- When it’s time to split the beehive into two because it’s become too large (known as swarming)
It might surprise you to learn that the queen bee has little to no say in any of this. Most of the decisions are made for her while she focuses on laying eggs. As the queen gets older, her egg-laying ability declines, and the worker bees sense this.
And as a result?
The worker bees start raising new queens to take the old queen’s place.
What happens next?
In honeybee colonies, the newly hatched queen will kill off the old queen and replace her as the new royal highness.
Related: Do Bees Have Knees?
3. Worker bees (and queens) are the only bees that can sting
Meaning, only female bees can sting. Male bees aren’t equipped with stingers, so they’re not always the most useful for defending the hive.
There are exceptions, however.
For example, male carpenter bees defend their nests, even though they don’t have stingers. (Some people call this “all talk, no action”).
Female carpenter bees build nests while male carpenter bees buzz around the nest to scare off intruders. This technique is called “dive-bombing,” and it’s very useful for fending off predators.
Related: Do Sweat Bees Sting or Bite?
4. Worker bees are the smallest bees in the hive
Worker bees are proof that good things come in small packages.
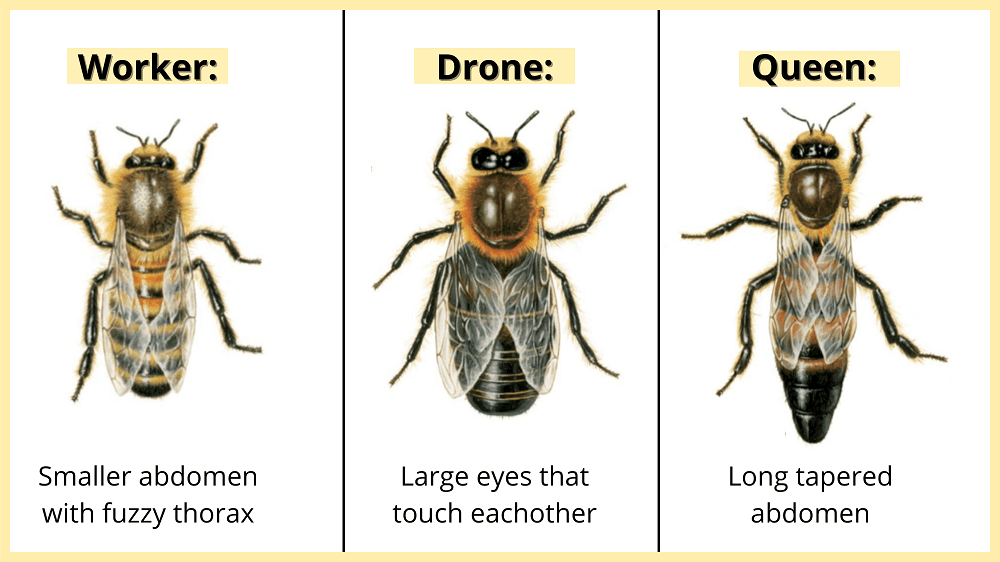
If you take a peek inside a beehive, you’ll notice that worker bees are slightly smaller than the drones and queen bees. But like other bees, worker bees still have a head, thorax, and abdomen.
Worker bees are also equipped with long tongues to suck the nectar out of flowers. The length of a bee’s tongue varies depending on the species. For example, certain species of bumblebees are known for having longer tongues than honeybees. A longer tongue allows bumblebees to reach nectar from certain flowers better than other bees.
FAQs about “Are Worker Bees Male or Female?”
- Are worker bees all female?
- Are worker bees males?
- Are there male worker bees?
- Do male bees do any work?
Are worker bees all female?
This is a common question we get, alongside other questions such as:
What is a female bee called? What gender are worker bees? Are worker honeybees male or female?
The answer:
Worker bees are exclusively female bees. This is true for all bee species.
Worker bees live up to their name because they do the majority of the work for the hive. This includes collecting nectar and pollen from blossoms and cleaning, expanding, and protecting their nests.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “Are Worker Bees Male or Female?”
More to Explore:
Are worker bees males?
No, worker bees are female bees only. Male bees are called drones.
Drone bees have one sole purpose: to mate with new queens. Some drone bees die immediately after mating. Drone honeybees are an example.
However, many drone bees species can mate multiple times without dying, such as drone bumblebees.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “Are Worker Bees Male or Female?”
More to Explore:
Are there male worker bees?
No. Male bees are called drones, and they have entirely different jobs than female worker bees.
Worker bees do the heavy lifting for the hive while drones relax around until it’s their time to mate with a queen. But, not all drone bees get the luxury of mating with a queen. Only the fastest drones get the chance.
This means it’s possible for drones to never mate.
Either way, drones have a short lifespan, and they eventually get booted from the nest by worker bees. This is because most drones don’t contribute much by the way of food or protection. So worker bees don’t want drones hanging around using up valuable resources.
But as mentioned, there are exceptions.
For example, male carpenter bees don’t have stingers, but they do watch over their nests. They buzz around intruders to scare them away, making them more productive than other types of drones.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “Are Worker Bees Male or Female?”
More to Explore:
Do male bees do any work?
Yes and no.
It depends on the bee species. In honeybee hives, drones don’t do much besides eating and relaxing. And when it’s their time to mate, they die immediately afterward.
Other bee species, like male carpenter bees, do some work which includes being the security guard for the nest. They guard the burrow and watch for potential threats. If you walk close to their nest, they’ll buzz around you quickly to scare you off.
Despite the big showdown, male carpenter bees don’t have stingers. Only female bees do. But that doesn’t stop them from trying.





