Table of Contents:
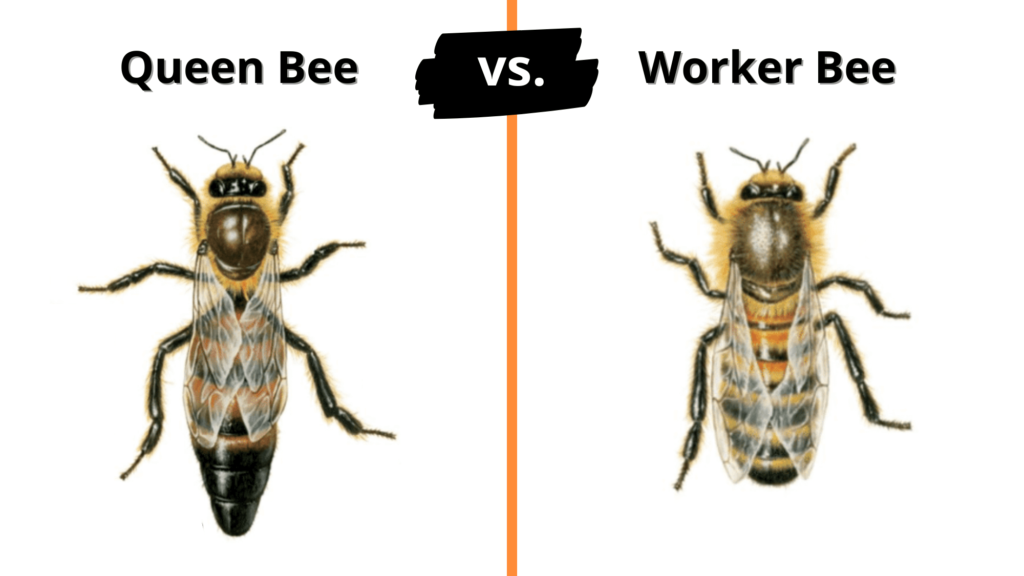
What’s the Difference Between Queens and Workers?
| Queen Bee | Worker Bee | |
|---|---|---|
| Image |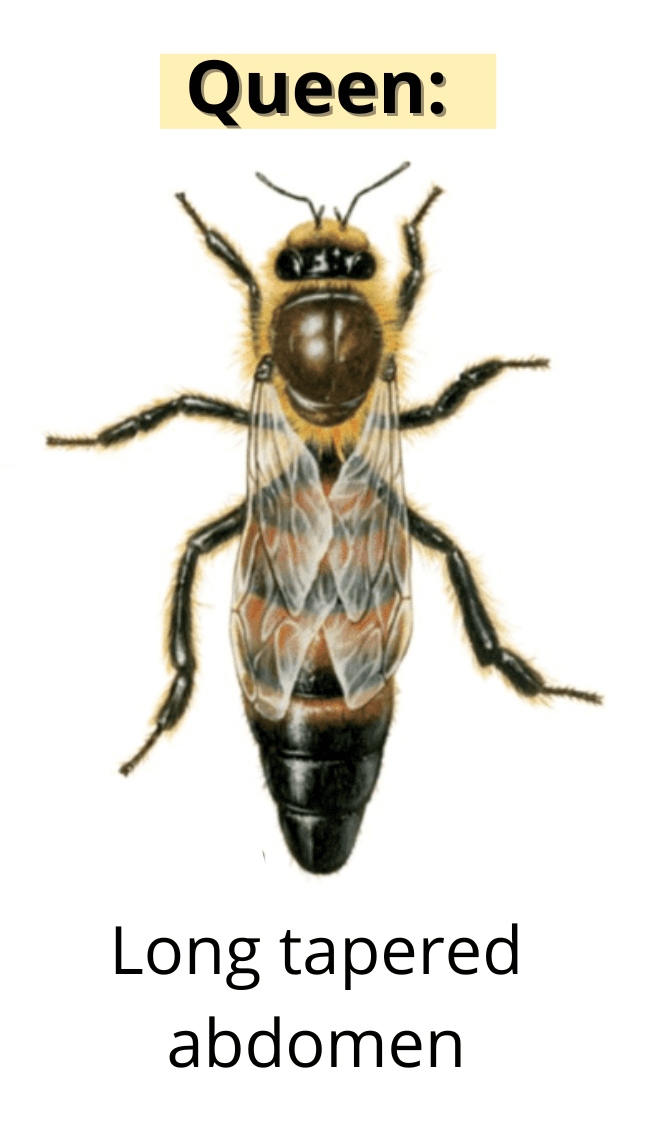  |
 |
| Size | Largest bee in the colony | Smallest bee in the colony |
| Lifespan | 2-4 years | 6-24 weeks |
| Job duties | To lay eggs and release pheromones | Collect food, make honey, defend the hive, make beeswax, tend to the queen & baby bees |
| Sting | Can sting humans several times | Can sting humans only once |
| Gender | Female | Female |
What Does the Queen Bee Do?

The queen honeybee has one primary job:
To ensure that the colony survives.
She does this by laying up to 2,000 eggs per day.
During the summer, a beehive can lose up to 1,000 worker honeybees daily. Worker bees have shorter lifespans than the queen, sometimes only living for four to six weeks. As a result, the queen bee stays busy trying to replenish these losses.
So you know what that means?
The queen simply doesn’t have the time to collect food, protect the hive, or build honeycomb. These jobs are left up to the worker honeybees.
You see, worker honeybees are called ‘worker bees’ for a reason. Worker bees are exclusively female bees that are responsible for the hive’s heavy lifting.
There can be upwards of 50,000 worker bees in a single honeybee hive. In most cases, there is only one queen bee per hive.
And while the queen is busy laying eggs, the worker bees feed, clean, and protect her. Worker bees also make honey, tend to the baby bees, and ward off potential predators.

Now here comes the big question:
Does the queen bee control the hive?
Not quite.
But it’s easy to hear the title “queen” and assume that she’s the supreme ruler of the colony. This isn’t the case at all. Instead, honeybee hives work more like a democracy where the worker bees make all the decisions.
For example, when the worker honeybees notice the queen is underperforming due to her age, they’ll replace her with a new queen. She has no say in the matter.
And what happens next?
The new queen hatches and has to duke it out with the old queen. They fight by stinging each other repeatedly until one of them dies. The winner declares victory and claims the ‘queen’ title.
So, in a nutshell:
The queen is like the puppet of the hive. Her main job is to lay eggs. The worker honeybees ensure she’s living up to that job; if she’s not, she gets the boot. It sounds rough, but it’s how nature intended it to be.
Can a Worker Bee Become a Queen?

Worker bees are hatched as workers and remain that way their entire lives. It’s the same for queen bees. Queens are hatched as queens and stay that way.
But this is what confuses people:
Both the queen bee and worker bees are female. Male bees are called drones, and they only make up a small percentage of the hive.
So if worker bees are also female, then why can’t they become queens?
Simple.
Beehives are like well-oiled machines. Each bee has a designated role that it was born to perform. Worker bees work, queen bees lay eggs, and drone bees (males) mate with queens from other hives.
Take human society, for example.
Doctors specialize in medicine. Lawyers specialize in law. Accountants specialize in taxes.
If a doctor suddenly had to take on the role of preparing taxes, it would be complete chaos.
Bees are the same way.

A bee develops into a queen bee thanks to the efforts of the worker bees. The larva set to become queen bees are fed a special diet of “royal jelly.” Royal jelly is more nutritious than the food given to the worker larvae.
As such, this rich diet of royal jelly allows the larva to hatch into a fertile queen bee.
Remember:
The queen bee is the only sexually developed female in the colony. Because of this, she’s the only bee in the hive that mates with drone bees.
Worker bees, who are also female, are sexually undeveloped and can’t lay fertilized eggs – nor do they even mate with male bees.
So chances are?
If you see a honeybee outside the hive, it’s probably a worker bee.
Queen bees stay inside the hive because they’re focused on laying eggs. This means the duty of collecting food and water is left up to the worker bees, which explains why worker bees are always buzzing around blossoms.
FAQs on “Queen Bee Versus Worker Bee”
- Is the queen bee bigger than the worker bees?
- Do worker bees mate with the queen bee?
- What do worker bees do if a queen bee dies?
- Why do worker bees kill their queen?
- Do worker bees and queen bees get along?
- Are there more worker bees than queen bees in a hive?
- Do queen bees live longer than worker bees?
- Where do worker bees and queen bees live?
- Do queen bees and worker bees eat the same things?
- Do the queen bee and worker bees both drink water?
- Can worker bees and queen bees sting?
- Do worker bees fight with the queen bee?
Is the queen bee bigger than the worker bees?
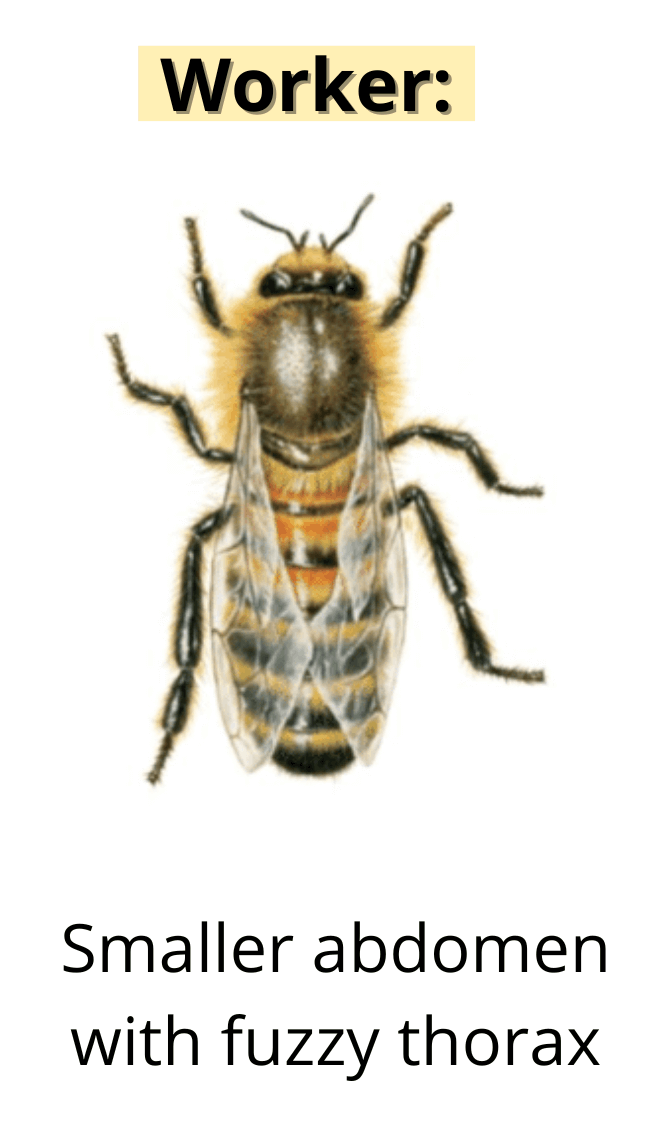
Yes, the queen bee is bigger than the worker bees. The queen bee can be up to 25mm long. This doesn’t sound very big, but it’s almost twice the size of the worker bees.
Worker bees are the smallest members of the colony. The queen is the largest, the drones are the second largest, and the worker bees are the smallest.
But keep in mind:
The size of a queen honeybee can vary between colonies. Her genetics, age, and diet contribute to the queen’s size. She’s noticeable because her abdomen is longer than the worker or drone bees.
The queen’s longer abdomen contains her reproductive organs. This includes a set of large ovaries that contains all the eggs.
But a smaller queen doesn’t mean she isn’t high-quality.
While bigger typically means better, sometimes newly mated queens appear small at first. But if you give them a few weeks to mature, their abdomen can start to plump up.
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
Do worker bees mate with the queen bee?
No, worker bees are actually female bees. This surprises many people because they assume that worker bees are either all male or a mix of male and female.
However, worker bees are exclusively female bees. Therefore, they cannot mate with the queen. Worker bees also don’t mate with male bees because that’s not their role inside the hive.
A worker bee has several job duties, including:
- Foraging for pollen and nectar
- Producing beeswax
- Making honey
- Warding off predators
- Cleaning the hive
- Protecting the queen
- Taking care of the baby bees
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
- How Are Queen Bees Made?
- How Long Do Bumble Bees Live?
- Honeybees vs. Bumblebees: How Do They Compare?
What do worker bees do if a queen bee dies?
A queen bee’s death is only a big deal if it happens unexpectedly. Other times, worker bees will prepare for the death of the old queen by raising a new queen to replace her.
But in the case where the queen dies suddenly?
For lack of a better term, the hive goes into ‘panic’ mode. They begin acting quickly to raise a new queen. This involves finding freshly laid larvae and feeding them the special ‘queen diet’ of royal jelly.
The worker bees work fast because their fate depends on having a queen bee. Queens are expected to lay thousands of eggs per day to keep the hive at a healthy population. Without her, the colony would eventually decline until all the bees die.
In some cases, the queen does die unexpectedly. For example, she might’ve accidentally gotten crushed by a beekeeper or killed by a predator.
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
Why do worker bees kill their queen?
Worker bees will reject the queen bee if they aren’t satisfied with her. A few reasons for this dissatisfaction include:
- She’s not laying enough eggs
- Her pheromones have declined
- The hive is stressed
- Something is wrong with her brood
- She’s damaged
- She’s a new queen they aren’t familiar with (such as an outside queen being introduced to a colony by a beekeeper)
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
- Ground Bees: Are They a Threat to Your Yard?
- Wasps vs. Honeybees: Are They Different?
- Do Bumble Bees Bite?
Do worker bees and queen bees get along?
Yes, worker bees have no choice but to get along with their queen because they rely on her for the colony’s survival.
But as mentioned, there are a few reasons why a colony may reject a queen. For instance, as she ages, her egg-laying abilities will decline. The worker bees will start raising a new queen bee to take her place.
In other bee species, like bumblebees, we see some conflict between the worker and queen bumblebees.
For example, worker bumblebees have been known to kill the mother queen. This can happen when the worker bumblebees want to lay eggs. However, worker bumblebees can’t lay fertilized eggs like queen bees can. They can only lay unfertilized eggs because they never mate with a male to collect sperm.
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
Are there more worker bees than queen bees in a hive?
Yes, worker bees make up the majority of the hive. There is (typically) only one queen bee per hive.
This means tens of thousands of worker bees can surround a single queen honeybee. Remember, honeybee colonies are large. They can have upwards of 50,000 bees in them.
A honeybee hive includes thousands of worker bees, typically a few hundred drones, and usually only one queen.
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
Do queen bees live longer than worker bees?
Yes, the queen honeybee has the longest lifespan out of any bee in the colony.
- Queen honeybee lifespan: 2-4 years
- Worker honeybee lifespan: 6-24 weeks
- Drone honeybee lifespan: 55 days
The average lifespan of a honeybee depends on many factors, including weather, climate, and predators. For example, honeybees may struggle more in cold-weathered climates. This is because bees are cold-blooded creatures that perform best in warm areas.
So in warm climates such as South America or Australia, bees can remain active all year round. In cooler climates, bees are forced to become less active during the winter. They have to huddle together inside their hive to stay warm.
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
Where do worker bees and queen bees live?
Queen honeybees and worker honeybees live together inside hives. Hives are made up of hexagonal-shaped wax cells that the bees build.
Bees use these cells to store honey, pollen, and eggs. The queen bee lays her eggs inside these cells.
Hives can be found in various places, including trees, walls, and man-made structures such as bee boxes.
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
Do queen bees and worker bees eat the same things?
They share similar diets, such as pollen, nectar, and honey. However, the queen bee gets an extra special substance known as ‘royal jelly.’ Royal jelly is a highly nutritious substance that helps the queen bee to grow and develop.
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
Do queen bees and worker bees both drink water?
Yes. Like people, bees need water to survive. They drink water to stay hydrated and to cool themselves down. Bees collect water from puddles, lakes, and flowers.
The only caveat is that bees can’t swim, so they have to be careful not to fall in the water and drown. This is why they perch themselves on the side of the water instead of landing directly on it.
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
Can worker bees and queen bees sting?
Yes, both worker bees and queen bees can sting. However, queen bees mainly only sting other queens when she’s trying to cement her role in the colony.
Queen bees rarely sting humans because they typically have little to no contact with humans. The exception is with beekeepers. Beekeepers will have contact with queens during their hive inspections.
But that said, the worker honeybees are there to defend the queen, so she doesn’t have to defend herself.
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”
More to Explore:
Do worker bees fight with the queen bee?
Worker bees will only fight with the queen bee if they reject her.
For example, sometimes beekeepers will introduce an outside queen to a beehive. This typically occurs when the colony is queenless due to an unexpected incident that killed the queen.
Sometimes the colony will accept the new queen immediately, while other times, they’ll reject her and try to attack her. As such, the beekeeper will work to try to get the colony to accept the new queen.
—> Go back to the FAQs “Queen bee versus worker bee”