Table of Contents:
What Eats Bees?

Many animals eat bees, including birds, skunks, bears, spiders, and wasps.
Some bee species, such as honeybees, are also targeted for their honey. For example, honey badgers are prime predators of honeybee larvae and honey. Honey badgers use their strong claws to climb trees and raid honeybee nests.
But here’s the thing:
Bee stings don’t affect honey badgers like they do humans.
You see, honey badgers have coarse hair that acts as a shield. They’re also covered in a thick layer of fat with loosely hanging skin that offers protection against stings. The same is true for bears, which are avid honey lovers that target beehives.
With that said, let’s cover some of the most common bee-eating animals:
Bee Predator #1: Spiders
One of the most common predators of bees is other insects.
As you can imagine, bees often get stuck inside spider webbing. However, not all spiders trap bees using webs.
Take crab spiders, for example.
Crab spiders don’t spin webs. Instead, they remain still and wait patiently – sometimes lying and waiting hours or days for their prey. They’re often camouflaged into their surroundings, so they go unnoticed.
As soon as their prey flies within reach, the crab spider jumps forward and injects a paralyzing chemical. Crab spiders feast on bees, beetles, butterflies, moths, wasps, and many other insects.
Bee Predator #2: Robber Flies
Robber flies are known for their predatory behavior.
They belong to a diverse group of predatory flies that usually perch in an open area, swiveling their heads to keep a lookout, then flying off to capture insect prey.
Once the bee is caught, the robber fly stabs it with its tongue and injects paralyzing enzymes into its body.
With that said, robber flies are equal opportunists and don’t just rely on bees for food. Robber flies have no problem chasing large insects like wasps, dragonflies, and hornets.
Bee Predator #3: Wasps

Even though bees and wasps are closely related, bees can still fall prey to wasps.
Wasps have large, scissor-like mandibles (jaws) that are made for capturing and tearing apart other insects.
Some species, such as the beewolf wasp (Philanthus bicinctus), are famous for hunting bees. They capture bees by stinging their thorax, paralyzing them, and bringing the bee back to their nest to feed their young.
Scientists believe that bumblebee decline in certain areas is directly related to beewolf wasps. Therefore, pollination is negatively affected in such areas.(1)
Bee Predator #4: Birds
Many species of birds will snack on bees as their protein source.
Summer tanagers are a type of bird found in the eastern and southwestern United States. These birds can eat their weight in bees and wasps, so they’re known as bee and wasp specialists. As such, you might hear them nicknamed the “bee bird.”
Summer tanagers are fast enough to catch bees and wasps in mid-air. Once caught, the birds hit their prey against a hard surface (like a branch) to knock off the stinger.
Besides insects, summer tanagers also forage for berries and fruit.
Bee Predator #5: Skunks

Skunks are nocturnal animals that eat bees at night.
They start by walking up to a hive entrance and scratching it. Once the bees fly out to investigate, the skunks swat at them, knocking them down so they can be eaten.
Skunks get stung, but like other bee predators, they can withstand a few stings for a quick meal. It’s not uncommon for skunks to get stung in the mouth as they’re trying to eat bees.
Bee Predator #6: Bears

Bears have a sweet tooth and love honey. In fact, it’s not uncommon for a bear to tear apart a honeybee hive in a matter of minutes.
Bears use a “snatch-and-go” method for grabbing honeycomb. They usually snatch off a huge chunk of the comb and run away. Meanwhile, the bees try to sting inside the bear’s ears and nose to deter them.
Bee comb provides bears with both carbohydrates and protein. The protein comes from the bee larvae inside the comb, and the carbs come from the honey.
Bee Predator #7: Predatory Pests

Ask any beekeeper you know, and they’ll tell you that one of the staples of raising healthy bees is killing pests that harm them.
Beekeepers face three common pests: hive beetles, varroa mites, and wax moths. Each of these pests can do a lot of damage to a bee hive.
Hive beetles are small beetles that feed on bee broods. They lay their eggs inside the hive, and when the larvae hatch, they eat away at bee larvae. This harms the population of the hive long-term.
Wax moths are another type of pest that eats beeswax, bee feces, the remains of bee larval cocoons, and bee cocoon silk.
Finally, varroa mites are a type of pest that attach themselves to honeybee bodies and feed off them directly. They weaken the bees, which can lead to the decline of the entire colony.
Are Bees Predators or Prey?
This is a tricky question because every ecosystem has a complex relationship between species.
Those that hunt and eat other species are called “predators.” Those that are hunted and eaten are called “prey.”
By following these definitions, bees are considered prey.
Unlike wasps, bees don’t kill other creatures to eat them. Instead, bees rely on pollen and nectar from flowers for food. In fact, flowers produce nectar to entice bees to pollinate them.
It’s a symbiotic relationship between bees and plants.
Flowers make nectar as a reward for pollinators, and the pollinators reward plants by helping them reproduce.
Does this mean that bees don’t kill things?
Not at all, actually.
Bees kill predators like yellowjackets, hornets, spiders, and other creatures trying to attack their nests. But they don’t kill the intruders to eat them. They do it for self-defense.
With that said, the terms “predator” and “prey” are regularly used to mean only animals that eat animals. But the same concept also applies to plants. For example, rabbits and lettuce have a predator and prey relationship.
Rabbits are considered predators, while lettuce is considered prey.
Of course, some animals are both predators and prey. For example, a wasp hunting for insects is a predator. If a bird eats the wasp, though, it becomes prey.
How Do Bees Defend Themselves?

Bees have a few different ways to defend themselves, their nest, and their colony.
The most common form of defense is stinging. Most bees have smooth stingers that allow them to sting several times without dying. Examples include bumblebees and carpenter bees.
But honeybees are the rare exception to this.
Honeybees have barbed stingers that can get stuck in animal or human skin. This kills the bee once it flies away because the stinger is ripped out of the bee’s body.
What’s more:
Social bees, like honeybees, often use a self-defense tactic known as “balling.”
Balling involves a group of bees surrounding an intruder into a tight ball and suffocating it to death. Japanese honeybees are known for using this technique against hornets.
In some cases, a bee’s best defense is to retreat.
For instance, solitary bees like mason bees or sweat bees are gentle creatures that fly away from threats instead of confronting them.
FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
- What are bees’ worst enemies?
- Will birds eat bees?
- Will wasps eat bees?
- Will hornets eat bees?
- What insects eat bees?
- What eats bees in the desert?
- Do chipmunks eat bees?
- Do bears eat bees?
- Do skunks eat bees?
- Do honey badgers eat bees?
- Do raccoons eat bees?
- Do honey bees have any predators?
- What really kills bees?
- Do hummingbirds eat bees?
- Do spiders eat bees?
- Do dragonflies eat bees?
- What animal would destroy a beehive?
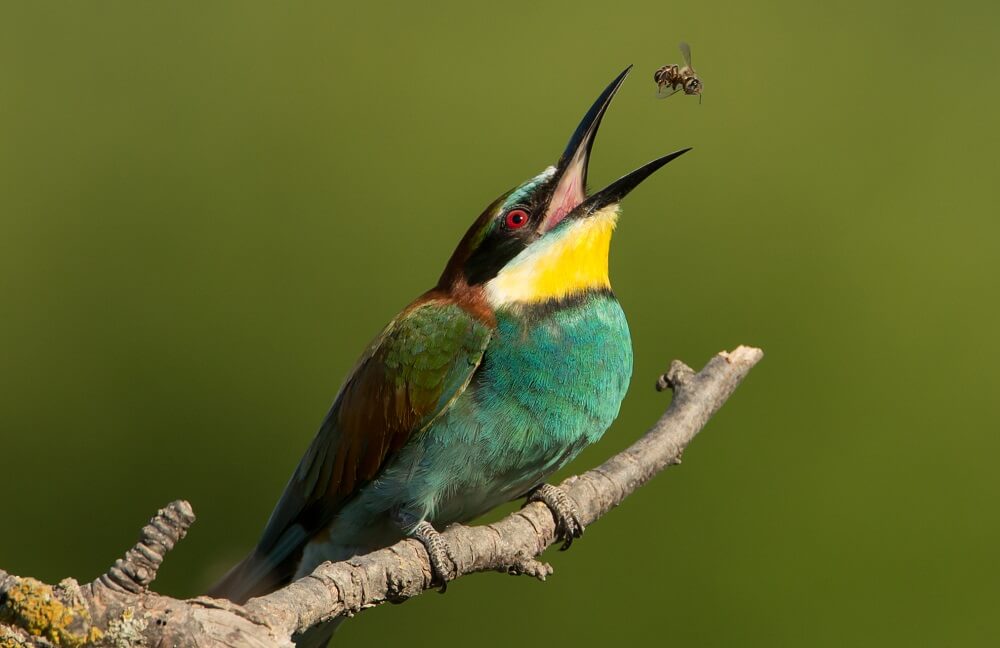
What are bees’ worst enemies? What is a bee’s natural enemy?
This depends on the species of bee and where they live.
For instance, bees that live in Europe are often hunted by birds known as bee-eaters. These birds are considered bee specialists.
Other predators of bees include wasps, hornets, spiders, skunks, and bears.
And unfortunately, humans are often considered threats to bees due to the use of insecticides and habitat loss.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
Will birds eat bees?
Yes, birds will eat bees. Birds also eat other insects, too. That said, some birds are considered bee specialists because they favor bees.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
Will wasps eat bees?
Yes, wasps eat bees and other insects for protein.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
Will hornets eat bees?
Hornets are types of wasps that eat bees.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
What insects eat bees?
Spiders, dragonflies, and wasps are all known to eat bees.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
What eats bees in the desert?
Scorpions are a type of animal that will eat bees if they can catch them. However, other animals in the desert, like lizards and snakes, will also eat bees if they come across them.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
Do chipmunks eat bees?
Yes, chipmunks sometimes eat bees, but they aren’t a common predator of them.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
Do bears eat bees?
Bears focus mainly on eating honey, but they do eat some bees and bee larvae in the process.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
- Ground Bees: Are They a Threat to Your Yard?
- Wasps vs. Honeybees: Are They Different?
- Do Bumble Bees Bite?
Do skunks eat bees?
Yes, skunks eat bees.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
Do honey badgers eat bees?
Yes, honey badgers eat both honey and bee larvae.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
- Do Carpenter Bees Pollinate?
- How Long Do Bumble Bees Live?
- Honeybees vs. Bumblebees: How Do They Compare?
Do raccoons eat bees?
Raccoon attacks on bees happen, but they’re less common than other predators.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
- Do Queen Bees Eat Honey?
- Are Worker Bees Male or Female?
- Queen Bee Versus Worker Bees – How Do They Compare?
Do honey bees have any predators?
Yes, honeybees have many predators, including birds, bears, wasps, hornets, and spiders.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
What really kills bees?
Many things can kill bees, including predators, harsh chemicals, and habitat loss.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
Do hummingbirds eat bees?
No, hummingbirds don’t eat bees. Their insect diet consists of aphids, ants, gnats, and small spiders.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
- What Kind of Bees Make Hives in Trees?
- Do Bees Fly in the Dark?
- Bees That Bite: Can Bees Bite Humans?
Do spiders eat bees?
Yes, spiders will eat bees if they can catch them. For example, it’s not uncommon to see bees caught in spider webbing. Some types of spiders, such as crab spiders, are known for ambushing bees.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
Do dragonflies eat bees?
Yes, dragonflies are predators of bees and other flying insects. They’re known for their quick reflexes and aerial hunting skills. Dragonflies have large eyes that allow them to spot prey from far away. When they see a bee, they fly quickly toward it and catch it mid-air.
—> Go back to the FAQs on “What Eats Bees?”
More to Explore:
What animal would destroy a beehive?
Many animals are known for destroying beehives, including bears, honey badgers, and honey buzzards. Animals are typically attracted to the honey in the hive. When they break into the hive, they will also eat the bee larvae. This can cause the hive to collapse.





