Table of Contents:
What is Bee Pollination?
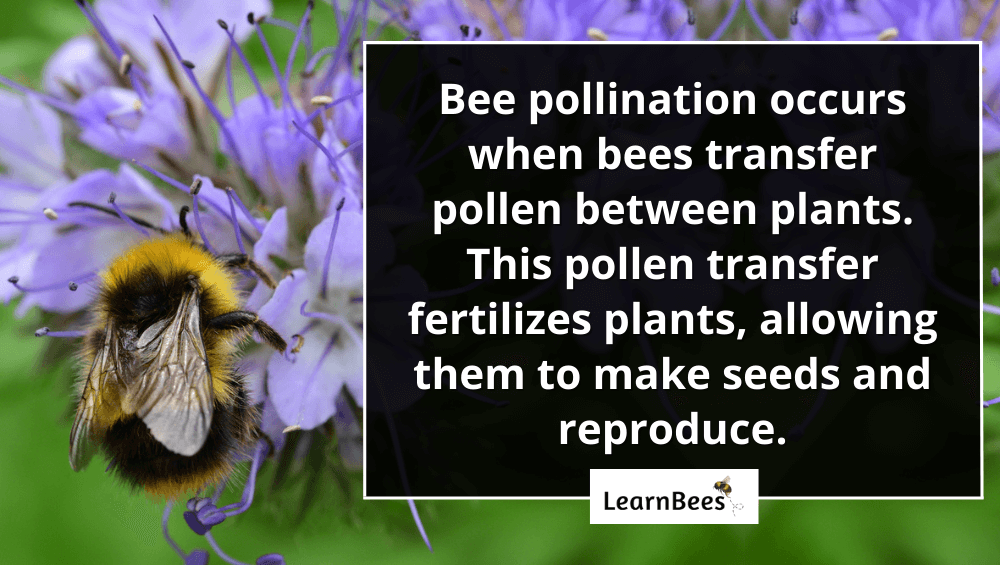
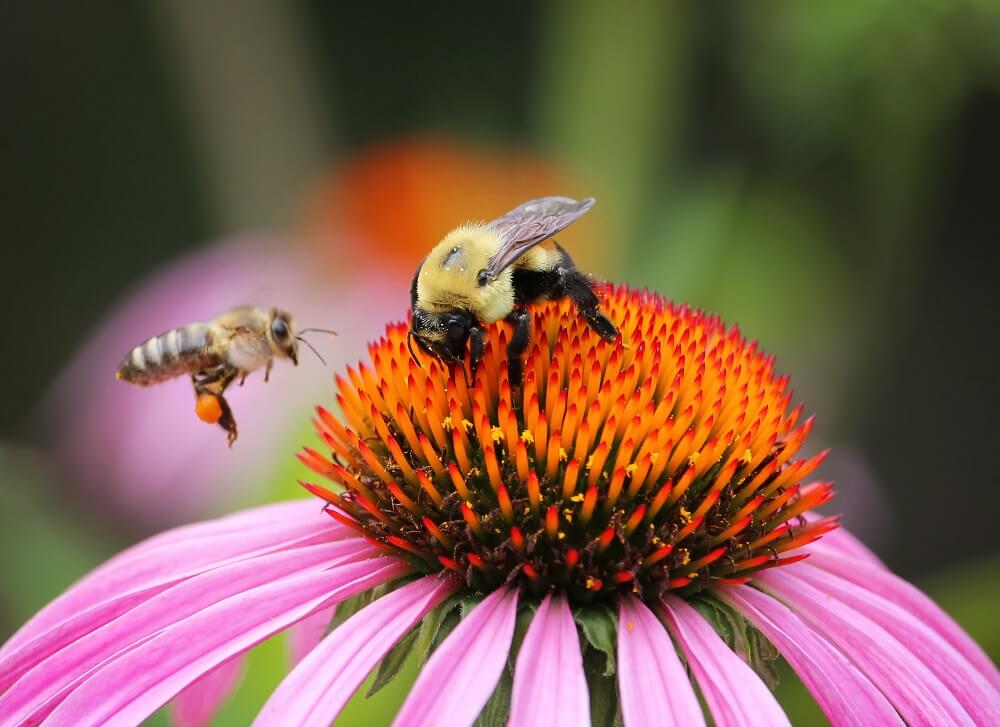
Bee pollination occurs when bees transfer pollen between flowers. The transfer of pollen leads to fertilization, allowing the plants to produce seeds.
But here’s the thing:
Pollination is beneficial for both bees and plants.
You see, a bee’s diet consists of pollen and nectar from flowers. Pollen is a powdery yellow substance that bees rely on for their protein source. Nectar is the sugary sweet liquid that bees rely on for carbohydrates.
So while many plants depend on bees for pollination, the bees also depend on plants for food.
Certain flowers are pollinator magnets, including salvia, lavender, and bee balm. Your garden will buzz with happy bees if you plant those in your yard.
Now the question becomes:
What are examples of bee pollinators?
Here are a few:
- Bumblebees
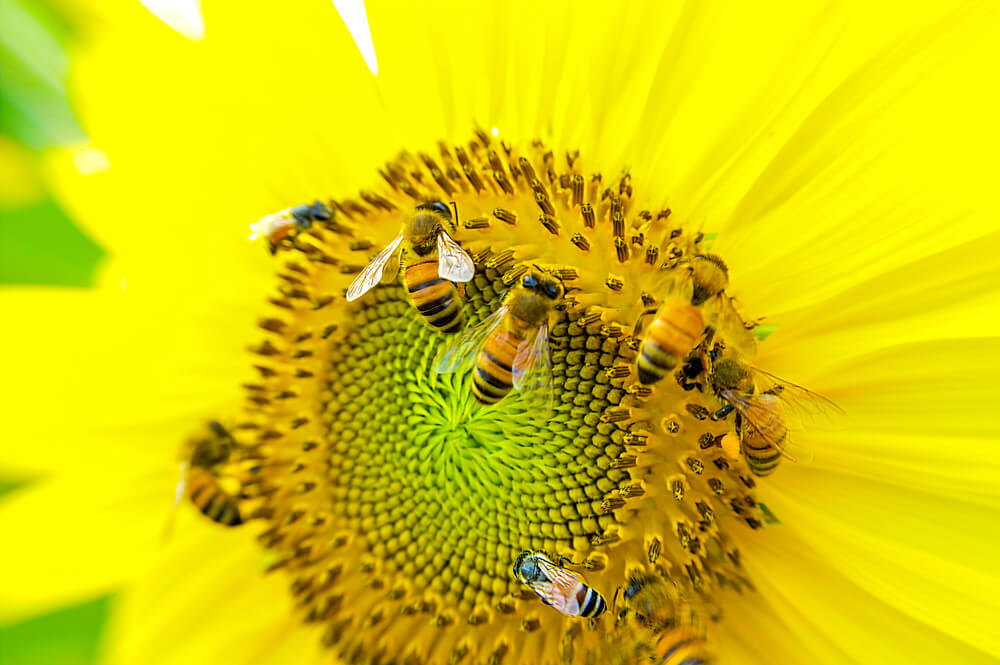
- Honeybees
- Carpenter bees
- Squash bees
- Sweat bees
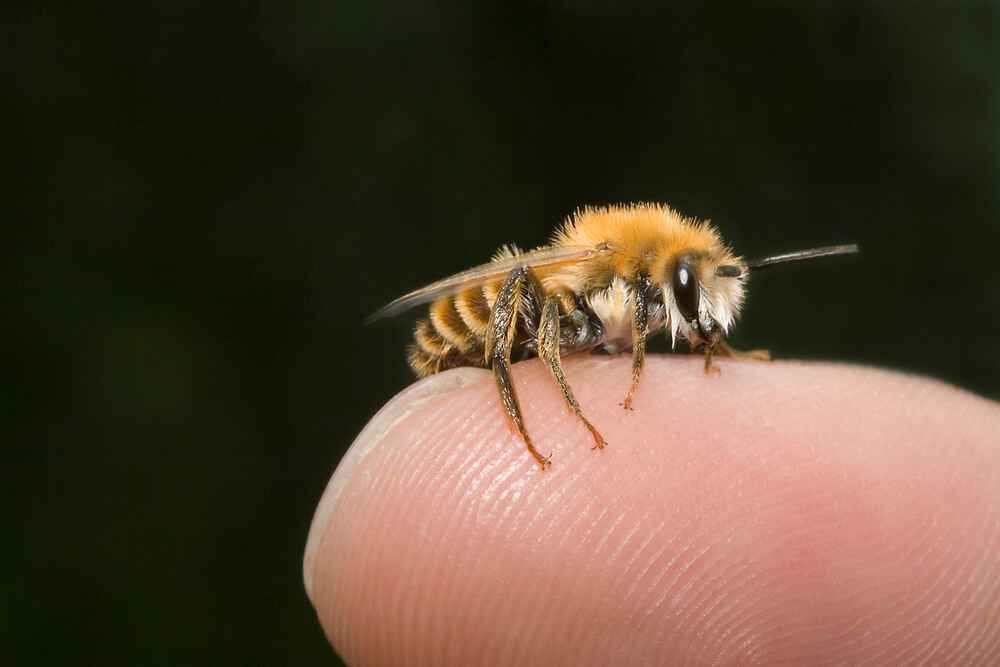
- Mason bees
- Leafcutter bees
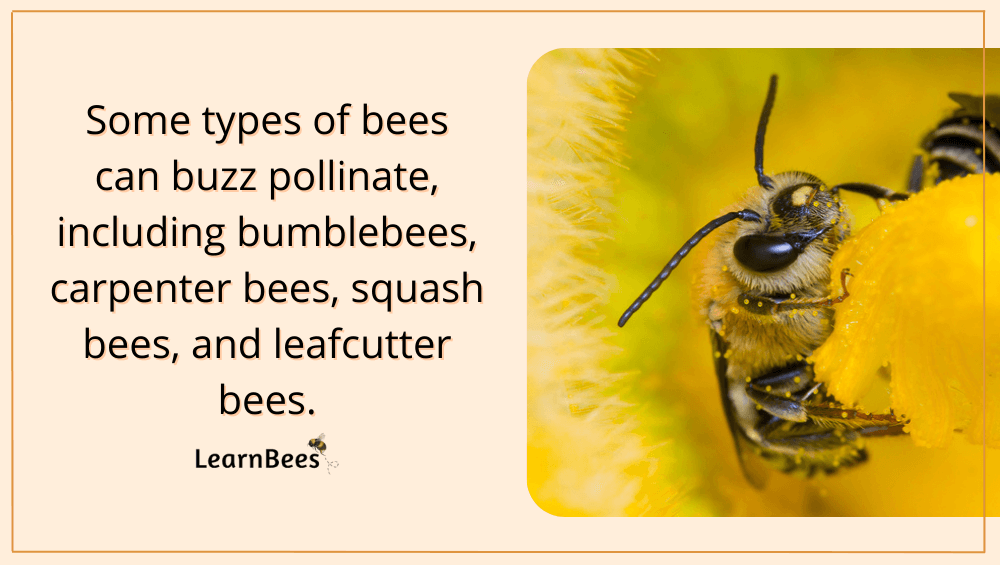
Even better?
Some types of bees offer buzz pollination. Buzz pollination is a type of pollination where bees rapidly vibrate their wings to get a flower to release pollen. They basically ‘shake’ the pollen out from the flower.
Why is this necessary?
Because some plants are more conservative than others when it comes to their pollen. Such plants have poricidal anthers, which means the pollen is packed tightly into the flower. As a result, most insects can’t access this pollen.
But this is where buzz pollinators come in.
Many types of plants require buzz pollination. Examples include blueberries, tomatoes, kiwis, and eggplants.
Interestingly enough, not all species of bees can buzz pollinate. For example, honeybees can’t buzz pollinate like bumblebees, carpenter bees, and squash bees can. With that said, honeybees are still important pollinators for our ecosystem.
In fact:
Pollinators are responsible for one in every three bites of food we eat.(1)
This includes bees, butterflies, bats, moths, beetles, hummingbirds, wasps, and many others.
Why is Bee Pollination Important?

Pollination is important because we rely on it for many of the crops we eat.
More specifically, pollination is necessary for plant reproduction. Since plants are rooted in place and can’t move, they rely on pollinators to help them transfer pollen.
This is known as cross-pollination.
Cross-pollination occurs when bees (and other pollinators) carry pollen from one plant to another, allowing the plant to make seeds. Seeds are vital for creating the next generation of plants, which creates food for the next generation of pollinators.
Without pollinators, so many plants wouldn’t be able to make seeds and reproduce.
As such, we’d experience a food shortage of certain crops like apples, blueberries, cranberries, almonds, broccoli, and many others.
More importantly:
Pollination is key to the success of global agriculture, not just making pretty flowers.
And without pollinators, humans would have to pollinate flowers manually which would be labor intensive and costly.
Do All Bees Pollinate?

No, not all bees pollinate.
For example, cuckoo bees are a rare type of bee that doesn’t pollinate. They don’t collect pollen from flowers. Instead, they ‘steal’ pollen from other bee species. Female cuckoo bees linger around other bees’ nests, waiting for an opportunity to slip inside to grab pollen.
That said, most types of bees are pollinators. Cuckoo bees are a rare exception.
And keep in mind:
There are over 20,000 species of bees.
Some bees, such as honeybees and bumblebees, are widely studied. Other types of bees, such as vulture bees, aren’t as widely studied and therefore have a lot of mystery surrounding them.
With that in mind, some bees are more efficient pollinators than others. For example, buzz pollinators like bumblebees and carpenter bees can pollinate a flower in a single visit.
But on the other hand?
It can take a honeybee 7-10 visits to a flower before pollinating it fully.
Additionally, it’s been estimated that it only takes about 400 mason bees to do the pollination work of 40,000 honeybees. However, honeybees are still incredible pollinators despite not being as efficient as other bees.
And keep in mind:
A single honeybee hive can contain upwards of 50,000 honeybees. So what honeybees lack in efficiency, they make up in size.
This is one reason why honeybees are commonly used for crop pollination. If you’ve seen beehives sitting on farmland, then you know a farmer has paid a beekeeper to help pollinate crops.
FAQs on Bee Pollination
- How do bees pollinate flowers step by step?
- What do honeybees pollinate?
- How does pollination work?
- What time of day do bees pollinate?
- What will happen if there is no pollination?
- How many flowers can a bee pollinate in a day?
- How many plants do bees pollinate?
- What is the best method of pollination?
- Can flowers survive without bees?
- How do bees know which flowers to pollinate?
- Do bees pollinate in the rain?
- Do bees pollinate in the snow?
- What kind of bees do not pollinate?
- What is the most important pollinator?
- How many species of bees pollinate?
How do bees pollinate flowers step by step?
- Step 1: Plants produce nectar to attract bees to their flowers so they can be pollinated
- Step 2: While drinking nectar, bees also collect pollen on their fuzzy bodies from the flower’s anthers (male part of the plant)
- Step 3: As the bee moves from plant to plant, some pollen grains fall off their bodies into the stigma (female part of the plant)
- Step 4: The fertilized plant later produces seeds as a result of being pollinated
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
- Do Queen Bees Eat Honey?
- Are Worker Bees Male or Female?
- Queen Bee Versus Worker Bees – How Do They Compare?
What do honeybees pollinate?
Honeybees pollinate various crops, including apples, blueberries, cherries, cranberries, cucumbers, almonds, and more. Honeybees also pollinate non-crops, such as sunflowers, lavender, salvia, and bee balm.
Honeybees are important pollinators because they’re one of the most common bees used for crop pollination. As such, they play an important role in global agriculture. Honeybees add more than $15 billion to the United States’ crop value.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
- Do Carpenter Bees Pollinate?
- How Long Do Bumble Bees Live?
- Honeybees vs. Bumblebees: How Do They Compare?
How does pollination work?
“What happens when bees pollinate flowers?” is a common question we get.
Flowers attract pollinators thanks to their nectar content, which is a sweet sugary substance that provides energy. While drinking the nectar, pollen gets stuck to the pollinator’s body. As a result, the pollinator transfers pollen between flowers as they fly around.
This is necessary for plant reproduction. Plants are rooted in the ground and cannot move, so they rely on pollinators to help them transfer pollen to other plants of the same species. This process is called cross-pollination, and it’s how many plants reproduce.
Pollination is important because:
- It gives us numerous fruits, vegetables, and nuts,
- It creates plants that provide half of the world’s oils, fibers, and raw materials;
- It encourages the reproduction of plants that help prevent soil erosion,
- It increases carbon sequestration
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
What time of day do bees pollinate?
Generally, bees are active during the daytime. It’s not uncommon for bees to work from sunup to sundown.
As the sun rises in the morning, it warms up the bee’s nest and prepares them for their day. They begin foraging on flowers for pollen and nectar.
But keep in mind:
Each bee in a beehive has a specific role. For example, forager honeybees are responsible for collecting pollen and nectar. In contrast, house honeybees are responsible for cleaning the hive and caring for the nest.
As a result, these bees have different jobs and work different hours.
So the short answer is this:
Bees pollinate during the daytime, from sun up to sun down. When it gets dark out, bees will go back to their hive.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
- Ground Bees: Are They a Threat to Your Yard?
- Wasps vs. Honeybees: Are They Different?
- Do Bumble Bees Bite?
What will happen if there is no pollination?
People often ask, “Why is bee pollination important?”
Without pollinators, we would experience an extreme shortage of many of our world’s crops. In fact, about 1/3 of the food we eat each day is a direct result of pollination.
So what would happen if there were no pollinators?
Well, without bees pollinating flowers, many plants wouldn’t be able to produce seeds. And without seeds, we wouldn’t have many fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
In addition, pollinators help to produce many of the world’s oils, fibers, and raw materials. So without them, we would be lacking in many of the products and materials we use daily.
Not to mention, pollinators play an important role in preventing soil erosion and increasing carbon sequestration. So without them, our environment would suffer in many ways.
In short, without pollinators, we would be in trouble. They play a vital role in our ecosystem and our daily lives. Humans would have to manually pollinate plants if we didn’t have pollinators. This would be a labor-intensive and costly operation.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
How many flowers can a bee pollinate in a day?
Bees can visit hundreds or even thousands of flowers per day, depending on the area. It’s been said that a single honeybee can visit 50-100 flowers during one foraging trip. Once the honeybee has collected enough nectar, they’ll transport the nectar back to their hive to make honey.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
How many plants do bees pollinate?
Bees are invaluable for the world’s agriculture. Pollination is essential to roughly 250,000 flowering plants that depend on pollinators to reproduce. Additionally, more than 90 crops rely on bee pollination.
How does pollination work?
Let’s discuss the parts of the plant first.
A flower’s anther is the male reproductive portion of the plant. The anther makes and releases pollen. A flower’s stigma is the female reproductive portion of the plant. The stigma is coated in a sticky substance that grabs and traps the pollen grains. This process is known as pollination.
In summary, bees are hardworking creatures who work day in and day out collecting pollen and nectar from flowers.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
What is the best method of pollination?
Buzz pollination is one of the most efficient ways for bees to collect pollen. During buzz pollination, the bee will grab onto the flower with its legs and vibrate its body. This process shakes the pollen loose from the anthers and onto the bee. The bee collects the pollen onto its body and transports it between flowers.
Buzz pollination, also called sonication, is efficient because it takes the bee less time to pollinate a plant fully. But not all bees can buzz pollinate.
For example, honeybees can’t buzz pollinate like bumblebees can. As a result, it can take a honeybee 7-10 visits to pollinate a flower fully. In contrast, bumblebees can often pollinate a flower in a single visit.
However, this doesn’t mean honeybees aren’t valuable pollinators. They simply aren’t as efficient as buzz pollinators like bumblebees, carpenter bees, and leafcutter bees.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
Can flowers survive without bees?
Most flowers cannot survive without bees and other pollinators. It’s estimated that more than 80% of the world’s flowering plants need pollination to reproduce.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
How do bees know which flowers to pollinate?
Bees use their antennae to sniff out the best nectar sources without having to test every blossom.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
Do bees pollinate in the rain?
Bees stay inside their nests during heavy rains and windstorms. This is because rain makes it difficult for them to fly and collect nectar. A large drop of rain can injure a bee easily due to their small size.
However, if it isn’t dangerous, bees will venture out in light rain.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
Do bees pollinate in the snow?
No, bees are cold-blooded creatures that don’t come out in the snow. Some species of bees hibernate, while others simply become less active and huddle together inside their nests.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
What kind of bees do not pollinate?
Cuckoo sweat bees are a type of bee that doesn’t pollinate because they don’t gather pollen from blossoms. Instead, they steal pollen from other bees. Female cuckoo bees linger around the nests of other bees until they get a second to slip inside and grab pollen.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
What is the most important pollinator?
All pollinators are important, but bees are known for contributing the most pollination to global crops.
—> Go back to the FAQs on Bee Pollination
More to Explore:
How many species of bees pollinate?
There are over 20,000 bee species. We don’t have exact numbers on how many of them pollinate. However, we can say that most bee species pollinate.
There are a few exceptions, such as cuckoo sweat bees, which aren’t pollinators.





