Table of Contents:
What Are the Four Stages of the Bee Life Cycle?
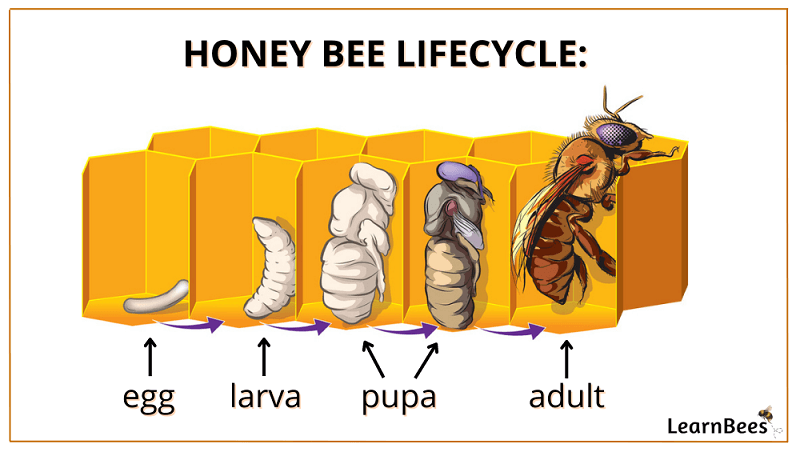
All bees undergo four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
Think about it like this:
Bees pass through a life cycle just like humans do. Humans develop from babies to toddlers to teenagers to adults. Meanwhile, bees develop from eggs to larvae to pupae to adults.
And you might be surprised to know:
Bees undergo a complete metamorphosis like butterflies and moths do.
Metamorphosis is the scientific way of saying “huge change.” It refers to how bees look totally different in the larva stage than in the adult stage. Much like how butterflies look incredibly different from when they were caterpillars.
Better yet?
Some bee species even spin cocoons around themselves before they pupate.
Cocoons are silky webs that offer protection. Think of a cocoon as a silk ‘sleeping bag’ some bees use before entering the pupa stage.
With that in mind, let’s discuss a bee’s life cycle in more detail. We’ll use honey bees as our primary example.
But one note:
All bee species pass through the four stages (egg, larva, pupa, and adult).
Honey bees are merely one example of a bee species out of more than 20,000. Common bee species examples include carpenter bees, bumble bees, mason bees, and sweat bees. Each of these different species shares the same four development stages.
Stage 1: Egg
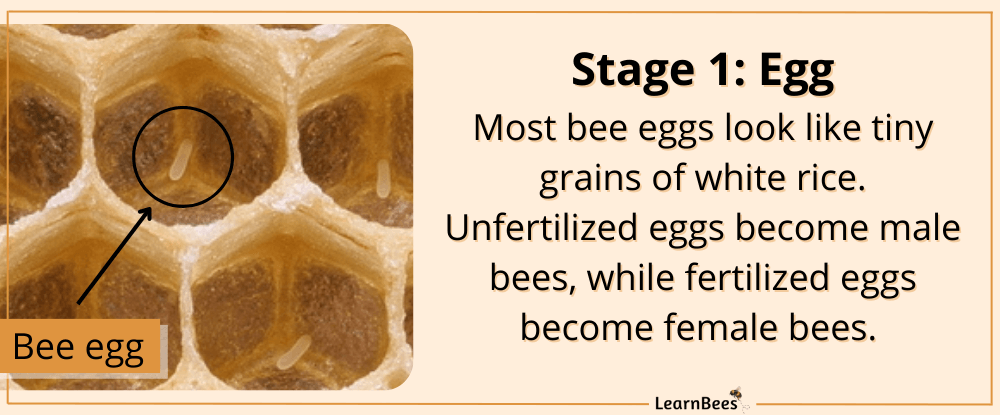
Bee eggs are laid by the female bee inside the nest. They look like tiny grains of rice under a microscope.
A female bee can lay hundreds or even thousands of eggs in her lifetime, depending upon the bee species. Queen honey bees, for example, can lay up to 2,000 eggs per day.
Meanwhile, female carpenter bees only lay between six and seven eggs in their entire lifetime.
Interestingly enough?
Female bees choose the sex of their offspring.
For example, if a mother bee wants to create a female bee, then she lays a fertilized egg. In contrast, she can lay an unfertilized egg to create a male bee. After a few days, the eggs hatch and develop into larvae.
Stage 2: Larva

After three days, the egg forms into a larva, which resembles a small white grub.
Bee larvae don’t have distinct eyes or legs, but they do have large mouths used for food. They also have small leg nubbins to move food around.
Here’s why:
A bee larva’s main job is to eat so it can develop.
In fact, a bee larva can grow to more than 1,500 times its original size within a few days. As the larva grows, it periodically sheds its outer skin. The skin shedding is called “molting,” and it helps the larva to grow larger each time it happens.
But bee larvae don’t all necessarily eat the same thing.
Queen honey bee larvae are fed a special diet of “royal jelly.” Royal jelly is an extra nutritious substance that allows queen honey bees to develop into queens.
Contrastly, other honey bee larvae are fed mostly honey and pollen.
Stage 3: Pupa
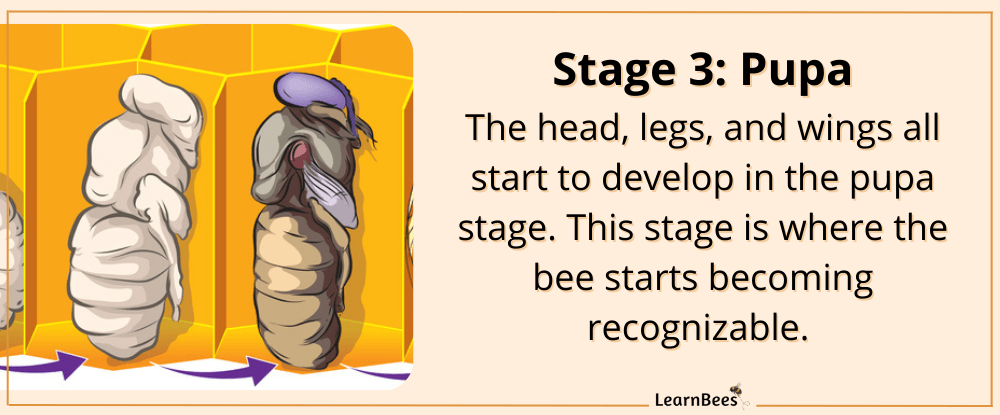
After about six days, the honey bee larvae are covered with beeswax inside a hexagonal cell. This is when the bee starts spinning a cocoon around itself to pupate.
It’s during the pupa phase that the bee starts becoming recognizable. The head, legs, wings, and abdomen all start developing. Additionally, the fine hairs or “fuzz” that coat the bee’s body develop.
And while all this is happening?
The female worker honey bees are responsible for tending to these baby bees. They feed, protect, and maintain the nest to ensure the future of the next generation of bees.
The pupa stage lasts seven to fourteen days, depending on the type of honey bee (queen, worker, or drone). After the pupa stage is complete, the adult bee is ready to chew itself out of the cell.
Stage 4: Adult
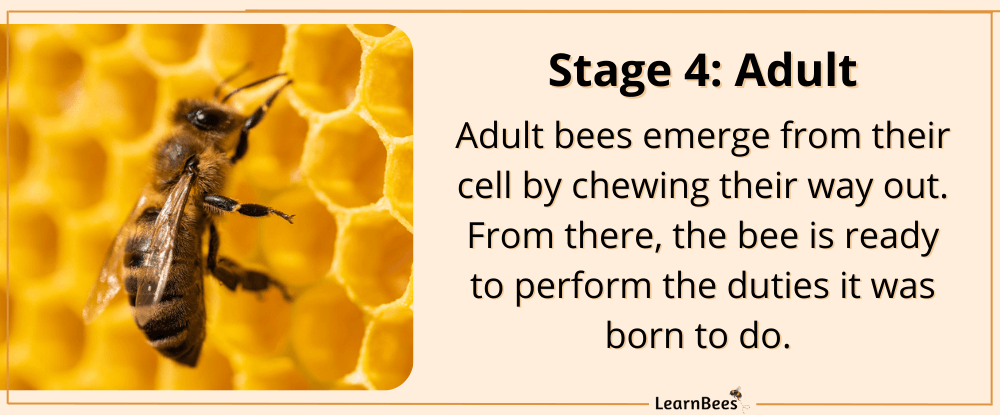
Adult bees are ready to fly as soon as they emerge from their cell.
But the length of time isn’t the same for all bees.
For example:
It takes queen honey bees about 16 days from egg to adult bee, whereas worker honey bees need 18 to 22 days to develop completely. Drone honey bees take the longest from egg to adult, coming in around 24 days.
The term “emerge” describes when adult bees chew themselves out of their wax cell.
Do Female Bees Get Pregnant?

Female bees don’t get pregnant. Instead, female bees reproduce by laying eggs which is known as oviparity.
How do they differ?
Pregnancy occurs when a developing embryo or fetus is carried within the female body. A successful pregnancy results in a live birth of a baby.
Oviparity involves animals laying eggs that hatch outside the female’s body. This reproduction method doesn’t result in a live birth. Instead, the eggs develop after the mother lays them.
Surprisingly enough:
Some female bees can lay thousands of eggs from only a single mating flight.
A “mating flight” occurs when a female bee flies near male bees to mate with them. Some female bee species only mate with one male bee, while others can mate with over 15 males.
For instance, queen honey bees can go on a single mating flight and mate with 15-20 drone honey bees. In fact, her goal is to mate with a high number of drones to ensure she collects enough sperm to lay eggs with.
Can Bees Lay Eggs Without Mating?
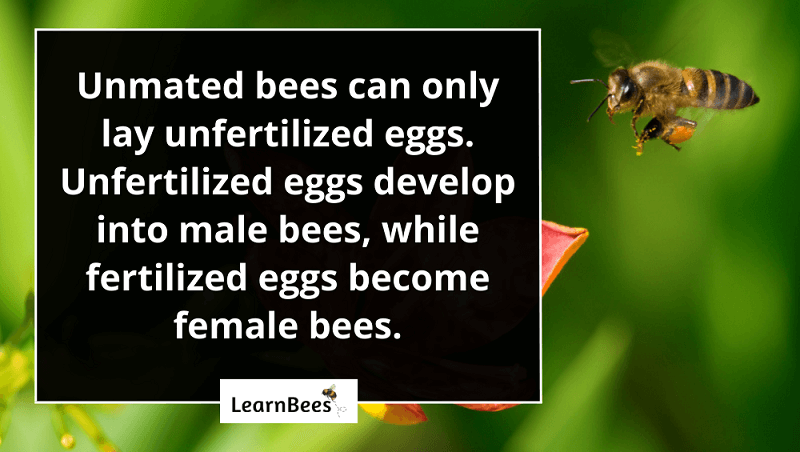
Unmated bees can only lay unfertilized eggs. Unfertilized eggs become male bees, while fertilized eggs become female bees.
But keep in mind:
You need both fertilized (female) eggs and unfertilized (male) eggs to ensure the future generation of bees.
A bee can only lay both types of eggs if she mates with a male. This is known as sexual reproduction. It helps balance out the number of male and female bees so there aren’t too many of one and too few of another.
With that said?
In social bee colonies, only the queen bee mates with males. The other females (worker bees) never mate; therefore, they perform other duties besides egg-laying.
Worker bees usually only lay eggs if their queen has died and they’ve failed to replace her. In this case, the colony is doomed to fail. Worker bees can only lay male eggs because they haven’t mated.
The only problem?
A colony cannot survive with only male bees.
Male bees have one simple yet essential job, and that is to mate with female bees from other colonies.
Besides that, most male bee species don’t perform any duties around the nest. The female worker bees are responsible for cleaning, protecting, and maintaining the hive.
So in a nutshell, both male and female bees are crucial to the colony’s survival
FAQs on the Life Cycle of a Bee
- What is the life cycle of a queen bee?
- How long does it take for a bee to turn into an egg?
- How long is a bee pregnant for?
- How many days does a bee live?
- Are bees born male or female?
- How many times can a bee mate?
- What are the four stages of the life cycle of a bee?
What is the life cycle of a queen bee?
Like other bees, a queen bee’s lifecycle goes from egg, to larva, pupa, and finally, adult. Depending on the bee species, queens can live for one year or longer. For example, queen honey bees live two to three years, while queen bumblebees only live one year.
—> Go back to the FAQs on the life cycle of a bee
More to Explore:
- How to Repel Bees Without Killing Them
- Carpenter Bee vs. Bumble Bee
- The Best Essential Oils for Bee Stings
How long does it take for a bee to turn into an egg?
Bees don’t turn into eggs. Instead, female bees lay eggs that later develop into adult bees. It takes about three days for a bee egg to hatch into a larva.
—> Go back to the FAQs on the life cycle of a bee
More to Explore:
How long is a bee pregnant for?
Female bees don’t become pregnant. Bees are oviparous animals that reproduce by laying eggs. Pregnancy involves a developing embryo or fetus being carried within the female body, while oviparity involves animals laying eggs that hatch outside the female’s body.
A female bee can lay as few as six eggs in her lifetime or as many as thousands of eggs in her lifetime. It depends on the bee species.
For instance, female carpenter bees may only lay six to seven eggs in their lifetime. Meanwhile, queen honey bees may lay over 500,000 eggs.
—> Go back to the FAQs on the life cycle of a bee
More to Explore:
How many days does a bee live?
The lifespan of a bee depends on several factors, including the species, the bee’s role in the nest, the climate, and so forth.
The average queen honey bee lives between two to three years. In comparison, worker bees only live five to six weeks during the peak seasons. Drone honey bees (males) can live for three to five weeks.
—> Go back to the FAQs on the life cycle of a bee
More to Explore:
Are bees born male or female?
Unfertilized eggs develop into male bees, while fertilized eggs develop into female bees. The mother bee decides whether to lay a male or female egg. She determines this based on the colony’s needs and time of year.
For instance, more male honey bees are needed in the spring because that’s the prime mating season. Once winter approaches, male bees are booted out of the colony because they no longer need to mate.
—> Go back to the FAQs on the life cycle of a bee
More to Explore:
- What Are Black and Yellow Wasps?
- How Long Do Bumble Bees Live?
- Honeybees vs. Bumblebees: How Do They Compare?
How many times can a bee mate?
Bees can mate one time or several times, depending on the bee species. Bumble bee queens usually only mate with one male, while honey bee queens can mate with 15 or 20 males.
Queen honey bees mate with more males because they must lay more eggs than other bee species. A single honey bee colony can contain more than 50,000 honey bees. To keep the population at a healthy size, the queen honey bee stays busy laying eggs day in and day out.
Once the queen honey bee ages and decreases her egg production, the worker honey bees will raise a new queen to take her place.
—> Go back to the FAQs on the life cycle of a bee
More to Explore:
- Wasps vs. Honey Bees: Are They Different?
- Are Worker Bees Male or Female?
- Queen Bee Versus Worker Bees – How Do They Compare?
What are the four stages of the life cycle of a bee?
The bee’s lifecycle consists of four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The egg stage is the first in a bee’s life cycle and typically lasts three days. Eggs are laid by the female bee and hatch into larvae. Larvae eat a lot of food while developing to grow in size.
Once larvae have grown enough, they enter the pupa stage. During this stage, the bee’s body changes and looks more like an adult bee. Depending on the species, the pupal stage can last a few weeks or longer.
Finally, the bee enters the adult stage, where it can fulfill its role in the colony. Adult bees have various functions depending on their sex. Males are drones, while females are either workers or queens.
Each type of bee has its own duties and responsibilities to help keep the colony alive.





